What is ionized water
To understand ionized water, let's start with its building blocks: H₂O, which is water. Water is made up of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. The hydrogen atom has one proton (positive charge) and one electron (negative charge), while the oxygen atom has eight protons and eight electrons. The way hydrogen and oxygen atoms combine forms water molecules and ions. Now, let's talk about ionization, which happens when atoms gain a positive or negative charge during chemical reactions. When water undergoes ionization, hydrogen gets ionized because it has only one electron, making it unstable. This creates hydrogen ions (H+), making the water acidic. On the other hand, hydroxyl ions (OH-) are formed when a hydrogen atom joins with an oxygen atom, making the water alkaline. Ionization occurs naturally in all drinking water, but for maximum benefits, some water is ionized through a mild electrolyzing process, separating it into acidic and alkaline components. This technology reproduces the natural process to enhance the water's health properties. The unique characteristics of ionized water are explained in the next section.
Process of water electrolysis
Case 1: Water Molecules
In the picture, there's a chamber with water and two electrodes, but the power is OFF. Some water molecules have turned into ions, represented as H+ and OH-.

When the power is switched ON, the water gets influenced by the electric field and breaks down into H+ ions and OH- ions, as shown in the figure. (Note: For simplicity, we're representing Hydronium ions, H3O+, as hydrogen ions, H+).
The H+ ions (positively charged) are attracted to the negatively-charged electrode called the Cathode. On the other hand, the OH- ions (negatively charged) are attracted to the positively charged electrode called the Anode, as shown in the picture.

Case 2: minerals
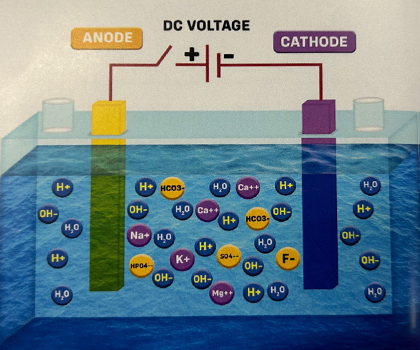
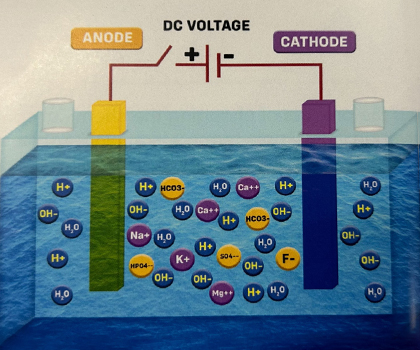
1. In the picture, there's a chamber with water and two electrodes, but the power is OFF. To make the electrolysis more efficient, some minerals like calcium, magnesium, sodium, potassium, sulfate, fluoride, bicarbonate, and phosphate are added to the water. This helps increase the water's ability to conduct electricity. So, it's better to use water with enough minerals (TDS Range 100-200 ppm) to act as an electrolyte.


2. When the power is switched ON, the mineral ions in the water get influenced by the electric field and move towards their respective electrodes. The Alkaline ions are attracted to the Cathode, and the Acidic ions are attracted to the Anode, as shown in the picture below.
Case 3
1. The picture shows a setup with an electrolysis chamber containing water with enough minerals, and the power is OFF.
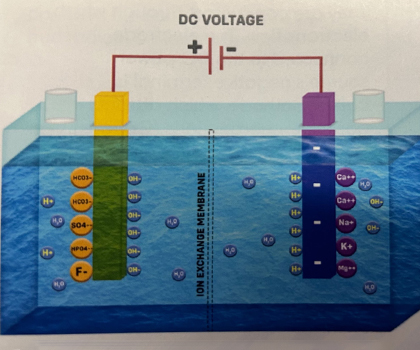
2. When the power is switched ON, some ions in the water are attracted to the Cathode. These include Hydrogen ions and Alkali ions like Calcium, Magnesium, Sodium, and Potassium. At the same time, Hydroxide ions and Acidic ions like Sulfate, Fluoride, Bicarbonate, and Phosphate are attracted to the Anode, as shown in the picture.
Cathode reaction
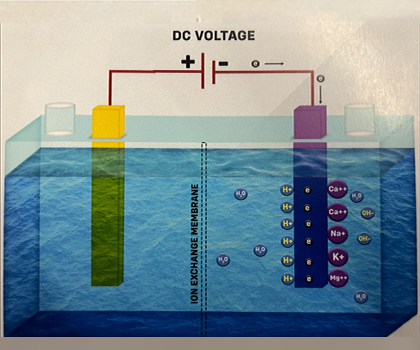
1. Looking at the Cathode reaction in Case 3, electrons are provided from the Power source to the Cathode, as shown in the diagram.When both Hydrogen ions (H+) and Alkali ions are attracted to the Cathode, the Preferential Discharge Theory comes into play. This theory states that the ion that discharges first is the one that requires the least energy or has a lower discharge potential.The order of ease of discharge of some common ions during electrolysis at the Cathode is as follows: K+ < Na+ < Ca²+ < Mg²+ < Al³+ < Zn²+ < Fe²+ < Pb²+ < H+ < Cu²+ < Ag²+ In this case, the alkali ions (K+, Na+, etc.) have a weak tendency to get discharged. So, Hydrogen ions (H+) discharge first by attracting electrons at the Cathode.
When Hydrogen ions gain electrons, they undergo a process called Reduction, which neutralizes their charge. The water collected at the Cathode is called "Electrolyzed Reduced Water.“ H+ + e- -> H
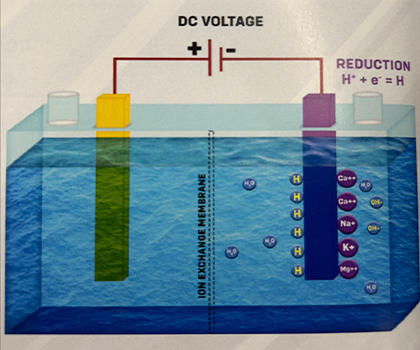
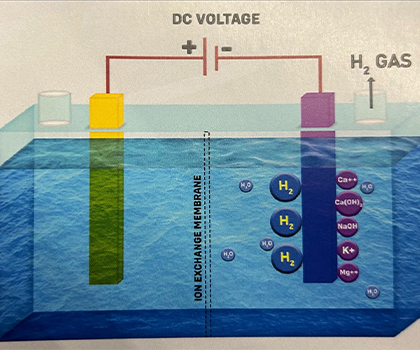
3. The unstable hydrogen atoms (H) quickly combine to form molecular hydrogen gas, H2. H + H -> H2 The H2 gas dissolves in water without changing its properties. At normal temperatures and pressure, water can hold about 1.6 parts per million (ppm) of hydrogen, which acts as a unique antioxidant in ionized water.Alkali ions attract hydroxide ions and form compounds like Calcium Hydroxide, Sodium Hydroxide, and so on.
Anode reaction
1.Looking at the Anode reaction in Case 3, Hydroxide ions (OH-) and Acidic ions (Sulfate, Fluoride, Bicarbonate, and Phosphate) are attracted to it. Both Hydroxide ions and Acidic ions can donate electrons, but in diluted solutions, Hydroxide ions (OH-) from water are discharged first. The order of ease of discharge of some common ions during electrolysis at the Anode is as follows: Fluoride ions (F-) < Sulfate ions (SO4²-) < Nitrate ions (NO3-) < Hydroxide ions (OH-) < Chloride ions (Cl-) < Bromide ions (Br-) < Iodide ions (I-).
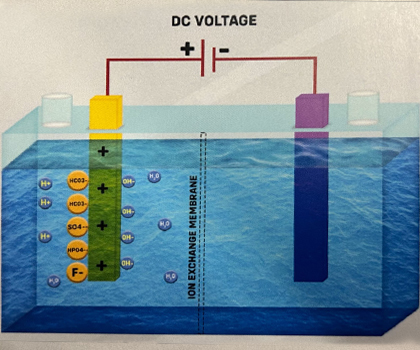
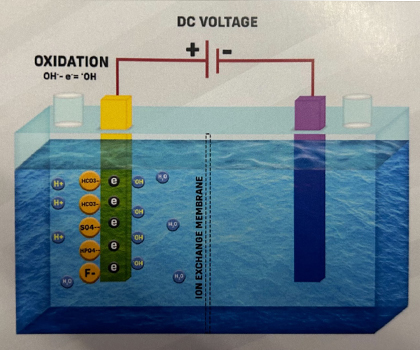
2.Hydroxide ions (OH-) donate electrons to the Anode and transform into Hydroxyl Radicals (-OH).
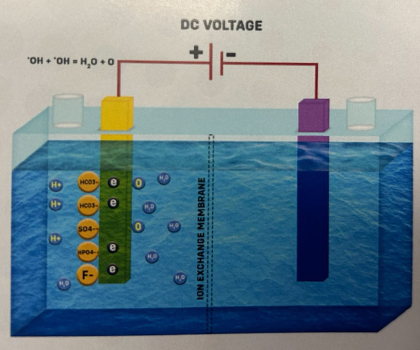
3. The Hydroxyl Radical (OH•), being unstable, rapidly reacts with another hydroxyl radical to form water (H2O) and Oxygen atoms (O). -OH + -OH -> H2O + O
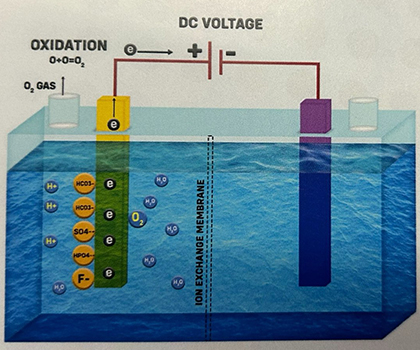
4. As the production of a single Oxygen atom (O) is unstable, it quickly combines with a neighboring Oxygen atom to form Oxygen gas (O2), which then dissolves in water. Hence, the water collected at the Anode is called "Electrolyzed Oxidized Water.“ O + O -> O2
5.Acidic ions attract hydrogen ions, and together, they form weak compounds like Carbonic acid (H2CO3), Sulfuric Acid (H₂SO4), and others.
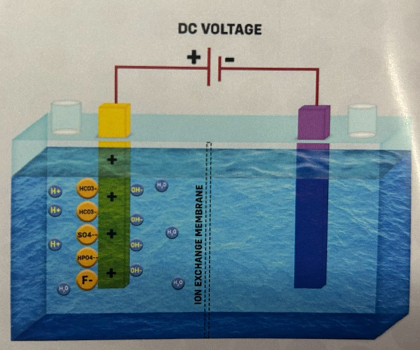
CATHODE
4H2O→4H+ 4OH-
4H2O+4e-
→4H+4e- + 4OH-
→2(2H++2e-) + 4OH-
4H2O + 4e- →2H2 (g) + 40H-
ANODE
4OH--4E- →2H2O+ O2
4H2O→4H++40H-
4H2O→4H+(2H2O+O2+4e-)
2H2O →4H ++O2(g)+ 4e-

Ionizer System
1.Before entering the ionizers, it is essential to ensure that tap water is properly filtered and contains enough minerals (TDS: 100-200ppm). To achieve this, some companies suggest using a primary filter that includes a Mechanical filter, Granulated activated charcoal, and calcium sulfite. This primary filter effectively removes rust, chlorine, sediment, volatile organic compounds, lead, as well as any unpleasant taste and odor from the tap water.


2.When the power is turned ON, the water flow activates the sensors, initiating the electrolysis process. The water collected from the primary hose (Cathode) contains dissolved molecular hydrogen (H2) and has a mildly alkaline pH range of 8-11. On the other hand, the water collected from the secondary hose (Anode) contains dissolved Oxygen and has a mildly acidic pH range of 4-6.
3.Ionizers typically include an ion-exchange membrane that acts as a barrier between two fluid streams known as Catholyte and Anolyte.
Molecular Hydrogen(H2)
Molecular hydrogen (H2) has gained increasing attention in recent years due to its potential health benefits for the human body. While research in this area is ongoing, several studies have suggested that molecular hydrogen may have antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and other health-promoting effects. Here are some of the potential benefits of molecular hydrogen for the human body:

- *Antioxidant Properties*: Molecular hydrogen is believed to act as a powerful antioxidant. It may help neutralize harmful free radicals in the body, which are unstable molecules that can cause oxidative stress and damage cells, proteins, and DNA. By reducing oxidative stress, hydrogen may contribute to overall cellular health.
- *Anti-Inflammatory Effects*: Chronic inflammation is linked to various health conditions, including heart disease, diabetes, and neurodegenerative disorders. Molecular hydrogen has been studied for its potential to reduce inflammation markers and mitigate inflammatory processes, possibly contributing to better overall immune function.
- *Mitochondrial Health*: Molecular hydrogen may support mitochondrial function, which is critical for energy production within cells. By maintaining healthy mitochondria, H2 could enhance cellular energy levels and potentially improve physical performance and stamina.
- *Neuroprotective Effects*: Some studies have suggested that hydrogen may have neuroprotective properties, potentially helping to protect nerve cells from damage and promoting brain health. This has implications for neurological disorders and cognitive function.
- Cardiovascular Health*: Research indicates that molecular hydrogen might have a positive impact on cardiovascular health. It could potentially improve blood vessel function, reduce blood pressure, and protect the heart from certain types of damage
- *Anti-Aging*: As oxidative stress and inflammation play a role in the aging process, the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of hydrogen might contribute to anti-aging effects.
- *Exercise Performance and Recovery*: Molecular hydrogen has been studied in the context of exercise performance and recovery. Some research suggests that hydrogen water may help reduce muscle fatigue and improve recovery after strenuous physical activity.
Oxidation Reduction Potential(ORP)
ORP is a measure of the tendency of a chemical species to gain or lose electrons and undergo oxidation or reduction in a given environment. it is commonly known as redox potential.
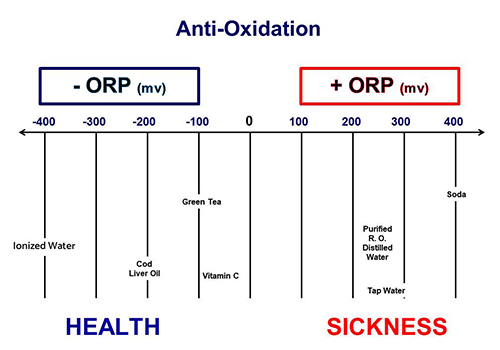
The orp value is expressed in millivolts.
- Oxidation : in an oxidation process is substance loses electron leading to an increase in its oxidation State this can be thought of as a loss of energy or an increasing positive charge.
- Reduction : in a reduction process a substance gain's electrons resultant in a decrease in its oxidation State this can be thought of as a gain of energy or a reduction in positive charge.
ORP values are measured on a scale in millivolts, with positive values indicating oxidizing conditions (electron-accepting environment), and negative values indicating reducing conditions (electron-donating environment). The ORP values can vary significantly depending on the specific chemical composition, pH, temperature, and other factors of the solution being measured.
In summary, oxidation-reduction potential (ORP) is a crucial parameter in understanding and controlling redox reactions in water treatment systems. It helps monitor the electron transfer potential and provides valuable information about the redox state of Water.
OXIDATION IS LOSSREDUCTION IS GAIN
Potential of hydrogen(PH)
pH stands for "potential of hydrogen." It is a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of a solution and is used to express the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) present in the solution. The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14, where:A pH value of 7 is considered neutral, meaning the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) and hydroxide ions (OH-) in the solution is equal.

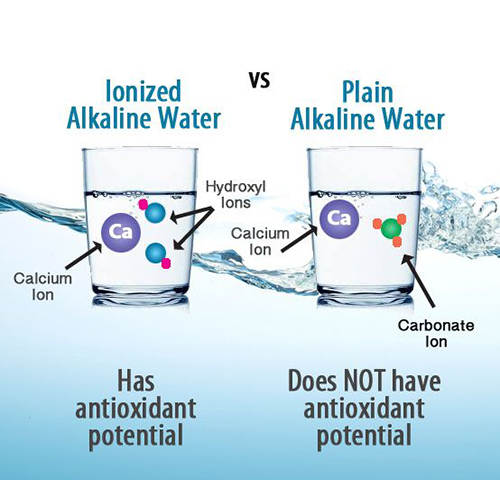
A pH value above 7 indicates alkalinity (basicity), meaning there is a higher concentration of hydroxide ions (OH-) than hydrogen ions (H+) in the solution.The pH scale is logarithmic, meaning each whole number change in pH represents a tenfold change in the concentration of hydrogen ions. For example, a solution with a pH of 3 is ten times more acidic than a solution with a pH of 4, and a solution with a pH of 10 is ten times more alkaline than a solution with a pH of 9.The pH level plays a critical role in the human body as it influences various physiological processes. The body carefully regulates pH levels in different fluids and tissues to maintain homeostasis, which is essential for proper functioning.
Micro-cluster
Water is made up of tiny clusters of molecules, not just one molecule. Tap water has larger clusters of about 15-20 molecules. These large clusters can reduce the body's need to drink water. On the other hand, "micro-clustered water" has smaller clusters of about 5-6 molecules, and it's better because it's said to be more soluble and hydrating. To get micro-clustered water, people may use a "water ionizer" machine, which breaks the electrical bonding of water molecules. This supposedly creates clean and healthy water that is fit for drinking.

How To Choose Water Ionizer
When choosing a water ionizer, pay attention to two main factors: the type of ionization plates and the power they receive. The plates come in three styles: solid, mesh, and slotted. The power per square inch affects the pH and ORP (Oxidation Reduction Potential) output. Higher power leads to better ion separation, resulting in higher pH levels and more negative ORP.
Types Of Plates:
The three types of plates used in water ionizers are solid, mesh, and hybrid. Solid plates are the traditional and robust option, but they have the drawback of focusing electricity on the outer edges, making them less efficient in generating antioxidants. Mesh plates are an advanced version with many edges that conduct electricity throughout, leading to more efficient electrolysis and better ionization. However, they are susceptible to wear and tear, and after prolonged use, they may function poorly. Hybrid plates, as the name suggests, combine solid and mesh designs. They have electrolysis distribution holes that create conductive edges, enhancing surface area without compromising durability. The hybrid plates offer unmatched water ionization due to their efficiency and durability. So, for the best balance of efficiency and longevity, the hybrid plates are a top choice!
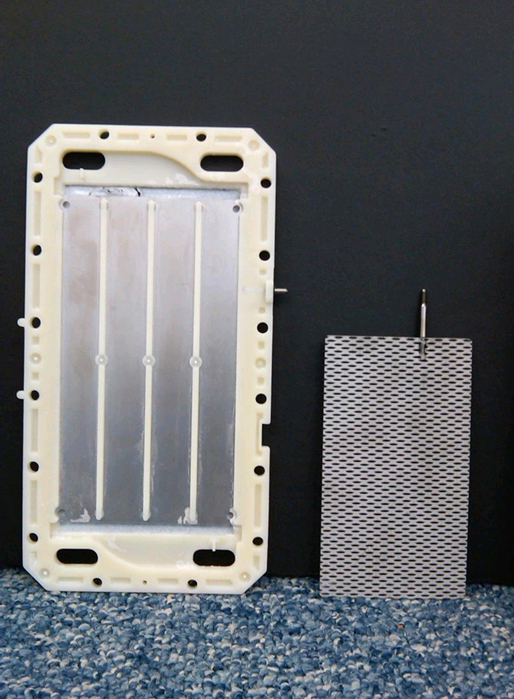
Myth About Platinum Coated Titanium Plates
Myth: Platinum-coated titanium plates pose a risk of poisoning, but this is a misconception. These elements are used in medical implants, and high-quality water ionizers use pure platinum titanium plates that do not disintegrate during electrolysis. Beware of Cheap Alternatives: Some low-quality ionizers use Platinoridium, a cheaper alloy of platinum and iridium, which can have adverse health effects. Avoid ionizers with electrodes coated with white gold, as they contain a significant amount of silver and are not suitable for drinking water. The Power of Plates: The number of plates in a water ionizer affects power consumption and water ionization. More plates can lead to better ionization and higher negative-ORP water for health benefits, but it also comes with a higher price tag. Plate size and material used are equally crucial factors .In essence, choose a water ionizer with pure platinum titanium plates and consider the number and size of plates along with their coating. Investing in a quality ionizer ensures efficient water ionization and optimal health benefits.
Types Of Power Supply
Power supplies in ionizers come in two types: switch-mode (SMPT) and linear. They both supply DC power, but their methods of producing it differ. A switch-mode power supply directly converts AC line power into DC voltage, resulting in a smaller, lighter transformer and higher efficiency. On the other hand, a linear power supply uses a power transformer to raise or lower the voltage, making it larger and heavier. Switch-mode power supplies are up to 80% smaller and lighter than linear ones, making them ideal for portable equipment. However, they generate high-frequency noise that can interfere with sensitive electronic devices. They can withstand small AC power losses without affecting outputs. Linear power supplies have larger semiconductor devices, generating more heat and lower energy efficiency compared to switch-mode. They offer faster transient response times, which is crucial for certain applications. In summary, switch-mode power supplies are great for portability and efficiency, while linear power supplies are robust and better suited for powering ionizer analog circuitry due to lower electrical noise. Each type has its advantages and disadvantages, making it essential to choose the right power supply based on the specific requirements of the ionizer's application.
Which Electrolyser Did I Choose: